SLA 99,95%: what this means and what is the responsibility of the cloud operator
20.09.2022
The success of cooperation between the customer and the service provider depends on a clear understanding of the capabilities of one and the expectations of the other. That is why it is customary to conclude a contract in the B2B market. However, complex technical services, such as renting cloud resources, are difficult to describe in a standard contract. Therefore, another document is signed – a Service Level Agreement (SLA).
What is SLA
Service Level Agreement is a document that defines the level of service expected by the client. The agreement sets out the characteristics against which the services will be evaluated and the remedies or penalties if the agreed service is not achieved.
The term appeared thanks to ITIL which sets a methodology for management, debugging and continuous improvement of business processes in IT. It is used by companies all over the world.
Every company that makes a decision to place its critical services in a virtual infrastructure, must understand how fault-tolerant it is, because the work of the business depends on it.
The agreement specifies in detail the obligations of the parties and the quality of the service. The client should not have any questions about what services the provider will provide and how.
The difference between SLA and OLA
Operational Level Agreement (OLA) is a document that describes the work of departments or units within the same company. For example, it specifies how the technical support service should respond to incidents and requests, what protocols should be used to start and run mission-critical applications, etc. And SLA describes cooperation with an external company.
To ensure the continuity of the service provision process, the provider must have both documents.
The main components of the Service Level Agreement
There is no single standard that defines everything that should be included in every agreement. Details will vary by industry, product type, specific individual arrangements, etc. The service agreement with the cloud operator should include the following:
- List and description of services provided by the provider.
- The scope and time of their implementation.
- Areas of responsibility of the provider and the customer.
- Technical support.
- Reporting requirements and service quality assessment metrics.
- Their cost, fines and terms of payment.
If we talk about the quality of service, it is important to include three main parameters.
Availability
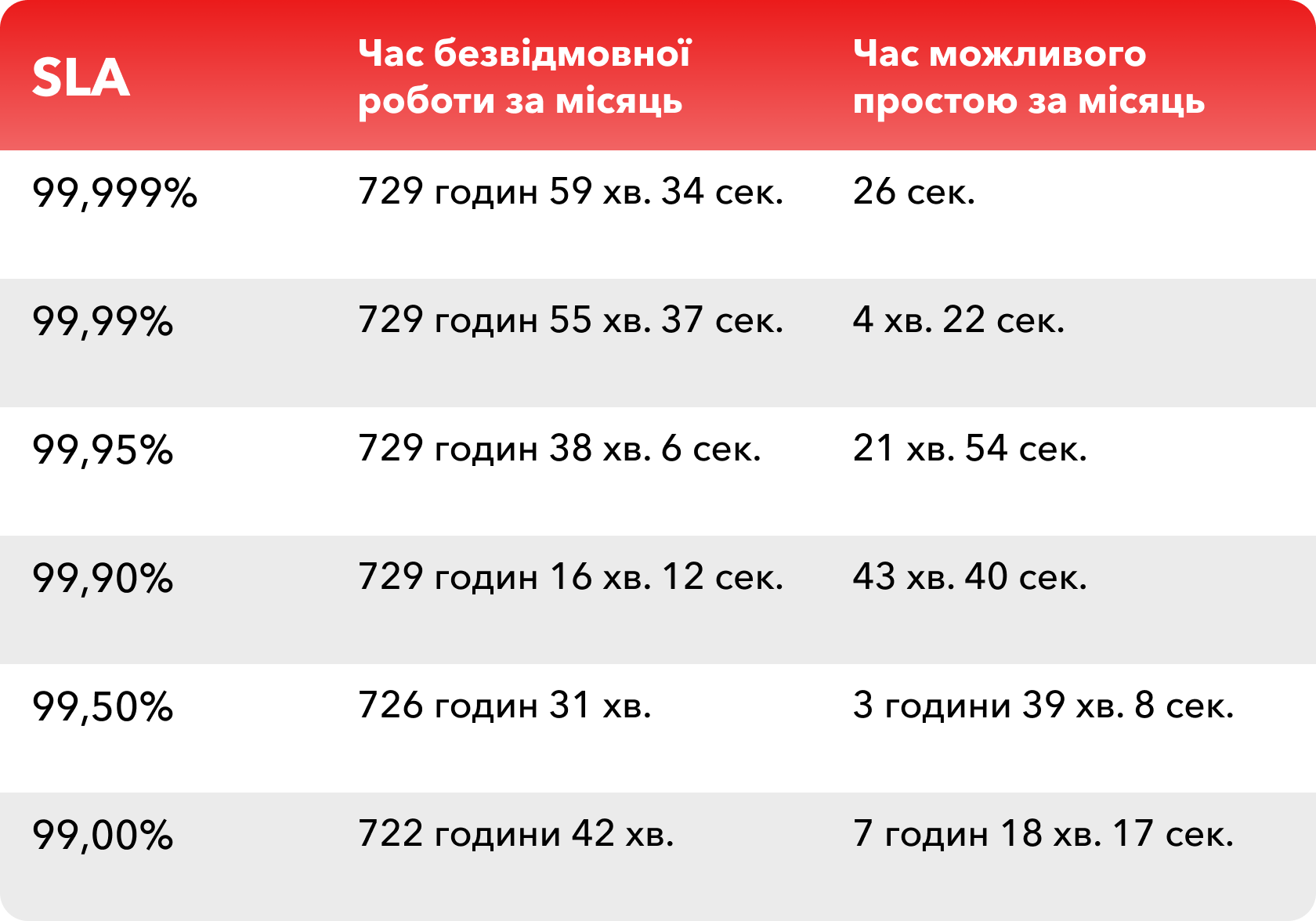
This is the expected uptime of the infrastructure, without taking into account scheduled technical work or downtime. This time is usually presented in the range of 99% up to 99.999%. The decimal places may seem like just a marketing ploy, but they are not.
There are approximately 730 hours in a month. When a cloud provider offers a 99.95% SLA, that means its infrastructure will be available for 729 hours, 38 minutes and 6 seconds. That is, the possible permissible downtime will be 21 minutes, 54 seconds.
GigaCloud provides a 99.95% SLA for a public cloud deployed on the VMware platform. It is built on the basis of four geographically dispersed data centres in Ukraine and the EU. This allows you to build fully redundant solutions and avoid a common point of failure.
Incident response time
This parameter means how much time will pass from the moment of receiving an error message, or from the moment of a signal from the monitoring system, to the start of work to restore the normal functioning of the service.
Incident resolution time
This is the maximum time from the moment the request is received by the provider's technical support service and during which specialists are obliged to perform the work.
Why is it not 100%
It is impossible to ensure 100% availability for several reasons.
First, the SLA of the cloud operator cannot be higher than the value guaranteed by the data centre in which it places its equipment. The reliability of data centres is determined by the Tier category. There are four of them, and they are expressed in percentages.- Tier I is about 99.67%;
- Tier II is 99.74%;
- Tier III is 99.98%;
- Tier IV is 99.99%;
Secondly, a failure can occur at the software level, which is not affected by the provider, because it is the responsibility of the customer.
For example, if a client application has 99.5% of availability, the infrastructure in which it is deployed has 99.95%, and the data centre in which the cloud "lives" is 99.98% available, then the combined availability will be no more than 99.5%. A secure geographically distributed cluster will not save an application that constantly "falls down".
Thirdly, the more nines are after the decimal point, the more expensive it will be to rent a virtual site. And not all IT services need such a protected and fault-tolerant cluster.
What will happen if the declared level is not met
Compliance with the SLA is a legal obligation of the operator, and if the promised level of service is not provided, then appropriate consequences should be provided for this.
Compensation for downtime occurs in the form of deducting the amount of compensation from the cost of services for the following month.
Advantages of Service Level Agreement for both parties
Having a contract provides advantages for both the operator and the customer.
For the client, the advantages are the following:
- The service is provided at the required level.
- A clear understanding of what you need to pay for.
- The ability to control the time of a request execution.
- No financial losses in case of incidents.
For the provider, the advantages are the following:
- The details of service provision and the estimated time for planned work and error elimination are clearly written.
- The process of interaction with the client is arranged.
- Levels of responsibility and critical parameters of service provision are determined.
- There is possibility to classify any server maintenance tasks.
The Service Level Agreement gives the customer confidence in the required level of service. However, the indicators prescribed in the document are lower than those that providers really aspire to. By specifying a minimum value of availability, they are actually working to increase it to the maximum.
Previously, we explained why a business needs a cloud, and what four most popular problems it helps to solve.





